| MONETARY POLICY | 22 | |
| Box 1: The MAS Core Inflation Measure for Singapore | 24 | |
MONETARY POLICY
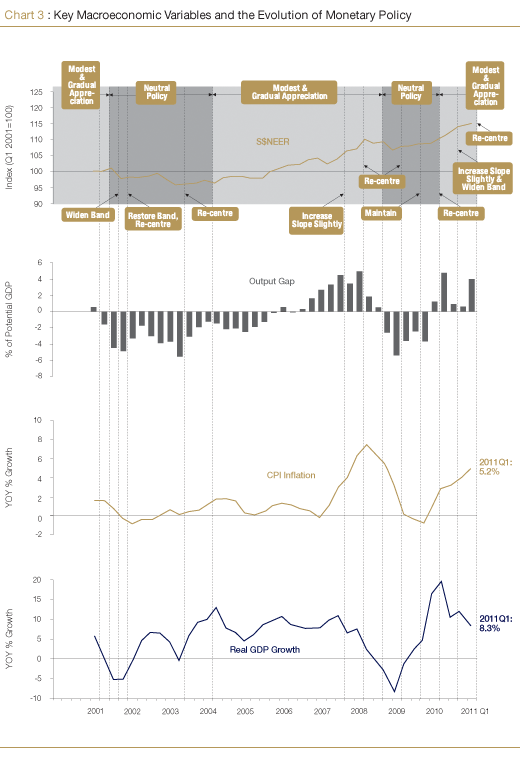
Singapore's macroeconomic policies are formulated with a medium-term orientation, and are aimed at promoting sustained, non-inflationary economic growth. Amidst the multiple shocks emanating from the external environment in recent years, monetary policy and fiscal policy have played a countercyclical role in smoothing volatility in the business cycle. Chart 3 traces the evolution of monetary policy, as indicated by movements in the S$NEER, against the backdrop of developments in growth and inflation. MAS' policy responses to recent global developments underscore the importance of the S$ as an anchor of stability.
In 2010, the output gap turned positive as the economy recovered decisively from the Great Recession to post record GDP growth. The macroeconomic policy stance was contractionary in 2010 as monetary and fiscal stimuli were gradually withdrawn, thereby ensuring that the policy setting was conducive to price stability and sustainable growth in the medium term.
MAS tightened monetary policy in April 2010 by re-centring the S$NEER policy band upwards and restoring its modest and gradual appreciation path. This policy shift marked the end of the accommodative monetary policy stance in place since October 2008. In October 2010, MAS tightened further by shifting to a slightly steeper appreciation of the S$NEER policy band without altering the level at which the band was centred. At the same time, the policy band was widened slightly to take into account volatility in international financial markets.
In April this year, the policy band was re-centred upwards to a level below the prevailing level of the S$NEER, with no change to its slope or width. This policy stance was to ensure price stability in an economy at a mature phase of expansion and to keep growth on a sustainable path. The graduated adjustment took into account MAS' previous pre-emptive tightening in April and October 2010, the effects of which will continue to filter through the economy over the rest of this year.
Amidst the turnaround in economic fortunes, the FY2010 Budget marked a shift in focus from crisis-containment to investment aimed at enhancing productivity over the medium to long term. The FY2011 Budget built on the robust economic growth in 2010 and introduced further supply-side measures targeted at restructuring the economy. These measures will lay the foundation for more sustainable and equitable growth over the longer term, and include initiatives to raise real income, support the economically vulnerable and reduce income inequality.